An algorithm is a finite set of instruction that if followed accomplishes a particular task.
An algorithm must satisfy the following rules:
Input :
There are zero or more quantities that are externally supplied
Output :
At least one quantity is produced.
Definiteness :
Each instruction is clear and unambiguous.
Finiteness :
If trace out the instructions of an algorithm ,then for all cases the algorithm terminates after a finite a number of steps.(finite number of steps)
Effectiveness:
Every instruction must be basic enough be corned out ,in principle ,by person using only pencil and paper .It is not enough that each operation be definite as ,it also must be feasible.
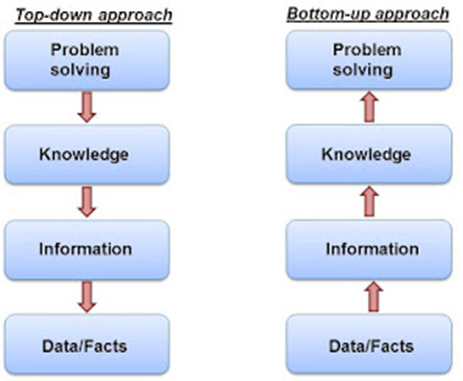
TOP-DOWN Approach :
- Definition:
The top-down approach is a problem-solving method where a system is broken into smaller, more manageable parts step by step. - Main Idea:
Start from the main problem (overall system) and divide it into sub-problems or modules. - Focus:
Focuses on the overall design first, then on the details of each part. - Process:
The solution is refined in stages — from general to specific. - Used In:
Commonly used in structured programming and software design. - Example:
To make software for a school — start with “School Management System” → divide into modules like Attendance, Exams, Fees, Students. - Comparison:
Opposite of Bottom-Up Approach, where small modules are made first and then combined.
Advantages:
- Easier to manage large projects.
- Promotes modularity and clarity.
- Helps in team collaboration
Disadvantages:
- May overlook lower-levels details intially
- Can be difficult to test early
In Short:
Top-Down = Think Big → Break Small → Implement Step-by-Step
TOP-DOWN approach (in simple language):
- Start from the Top — The process begins with the main problem or overall system.
- Break into Smaller Parts — The big problem is divided into smaller, easier sub-problems.
- Step-by-Step Detailing — Each sub-problem is then divided again until every part is simple to solve.
- High-Level to Low-Level — You first focus on the main structure, then move towards small implementation details.
- Planning First, Coding Later — In this approach, you first design the logic or structure before writing actual code.
- Used in Programming — Common in structured programming languages like C, where functions are planned from top (main) to bottom (sub-functions).
- Easier Debugging — Since the system is divided, it’s easier to find and fix errors in smaller modules.
- Better Understanding — Helps understand the system flow clearly — from general overview to specific steps.
- Code Reusability — Each smaller function or module can be reused in other programs too.
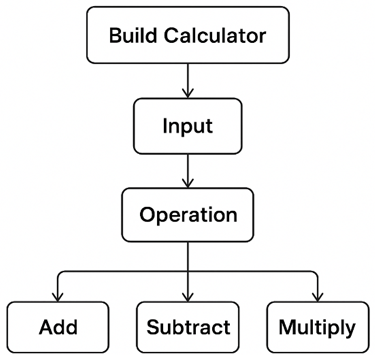
- Example — While building a calculator:
- Start → “Build Calculator”.
- Divide into → “Input”, “Operation”, “Display Result”.
- Then divide “Operation” → “Add”, “Subtract”, “Multiply”, “Divide”.
Example of top down Approach:
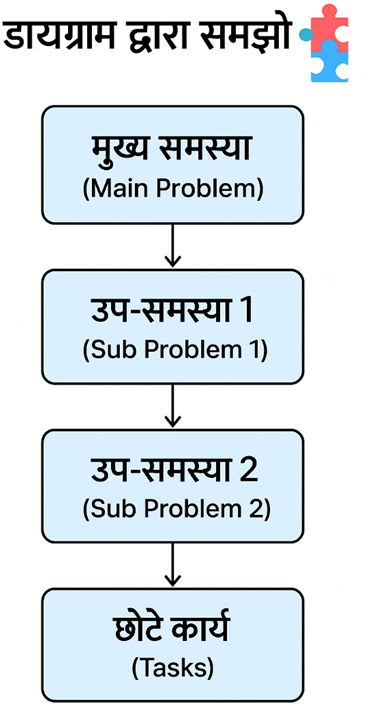
TOP-DOWN approach in Hindi Translation:
Top-Down Approach:-
🔹 1. Definition:
Top-Down Approach एक ऐसी तकनीक है जिसमें किसी बड़ी समस्या (Main Problem) को छोटे-छोटे भागों (Sub-Problems) में बाँटकर हल किया जाता है।
🔹 2. Easy Example:
मान लो तुम्हें एक वेबसाइट बनानी है —
पहले तुम पूरी वेबसाइट की रूपरेखा सोचोगे (Design + Features),
फिर उसे छोटे हिस्सों में बाँटोगे जैसे —
- होम पेज
- लॉगिन सिस्टम
- यूज़र प्रोफाइल
- डेटाबेस कनेक्शन
इस तरह बड़ी समस्या को छोटे टुकड़ों में बाँटकर काम करना ही Top-Down Approach कहलाता है।
🔹 3. Steps:
- समस्या को पूरी तरह समझो।
- उसे छोटे-छोटे हिस्सों में बाँटो।
- हर हिस्से पर अलग-अलग काम करो।
- सभी हिस्सों को मिलाकर पूरा सिस्टम बनाओ।
🔹 4. Use of top down approach:
यह तरीका सॉफ़्टवेयर डेवलपमेंट, प्रोग्रामिंग और प्रोजेक्ट प्लानिंग में बहुत काम आता है।
🔹 5. Advantages:
✅ समस्या को समझना आसान होता है।
✅ हर हिस्से पर अलग टीम काम कर सकती है।
✅ डिबग करना (Error ढूंढना) आसान होता है।
✅ काम का प्लानिंग स्ट्रक्चर साफ होता है।
🔹 6. Disadvantages:
❌ अगर ऊपर के डिज़ाइन में गलती हो जाए तो सब गलत हो सकता है।
❌ शुरुआती चरण में पूरा सिस्टम टेस्ट नहीं किया जा सकता।
🔹 7. Comparison:
यह Bottom-Up Approach के उल्टा होता है, जहाँ छोटे हिस्सों से शुरू करके बड़ा सिस्टम बनाया जाता है।8. Real Life Example:
अगर तुम्हें घर बनाना है,
तो पहले पूरी प्लानिंग (मैप) बनाओगे,
फिर अलग-अलग हिस्सों जैसे फाउंडेशन, दीवारें, छत, पेंटिंग आदि में काम बाँटोगे —
👉 यही Top-Down Approach है।
🔹 9. Conclusion:
Top-Down Approach एक ऐसा तरीका है जो समस्या समाधान और प्रोजेक्ट प्रबंधन को आसान बनाता है —
क्योंकि यह “बड़े से छोटे” की ओर जाता है और हर स्टेप को साफ तरीके से परिभाषित करता है।
BOTTOM-UP approach:
Bookkish language :
- A bottom up approach is just the reverse of top-down approach.
- Designing the most basic or concrete modules and then proceed towards designing higher level modules .
- The higher levels modules are implemented by using the operation performed by lower level modules.
- This Sub modules are grouped together to form a high levels modules.
- All the higher level modules are clubbed together to form even higher levels modules .This process is repeated until the design of the complete algorithm is obtained.
- Bottom-up-> apply on other hand defines a modules and then group together several to form a new highr level modules.
- It allows information hiding as it first identifies what has to be encapsulated within module and then provides an abstract interface to define the modules(boundaries as seen from the client).
Bottom -up Approach (in simple language):
- Meaning: In this approach, we start solving the smallest or simplest sub-problems first and then combine them to form the complete solution.
- Direction: It works in the bottom → up direction (from small to big).
- Focus: The focus is on building complex systems step-by-step from the base components.
- Used In: Commonly used in Dynamic Programming, Software Development, and System Design.
- Example: In DP (like Fibonacci series), we calculate smaller values first (F(0), F(1)) and then use them to find F(2), F(3)… etc.
- Coding Style: Code is written by first creating modules/functions for small tasks, then integrating them.
- Testing: Easier to test since each small part is verified before combining.
- Advantage: Reduces redundancy and helps in code reusability.
- Disadvantage: Harder to visualize the overall structure initially.
- Real Example: Assembling a car — first build small parts (engine, wheels), then combine them to form the complete car.
Bottom-Up Approach in Hindi Translation:-
- Definition इस पद्धति में हम सबसे पहले छोटे-छोटे हिस्सों (modules) से शुरुआत करते हैं और उन्हें जोड़कर एक पूरा सिस्टम बनाते हैं।
- Direction:काम नीचे से ऊपर (छोटे भागों से मुख्य सिस्टम तक) की ओर किया जाता है।
- Main Points: इसमें ध्यान छोटे मॉड्यूल्स या कंपोनेंट्स बनाने पर होता है, जिन्हें बाद में मिलाकर एक बड़ी प्रोग्रामिंग संरचना तैयार की जाती है।
- Example: जैसे कार बनाते समय पहले इंजन, टायर और बॉडी बनाई जाती है, फिर सबको जोड़कर पूरी कार तैयार की जाती है।
- कहाँ प्रयोग होता है: यह पद्धति ज़्यादातर ऑब्जेक्ट-ओरिएंटेड प्रोग्रामिंग (OOPs) में प्रयोग होती है।
- Integration: हर मॉड्यूल को अलग से विकसित और टेस्ट किया जाता है, फिर उन्हें एक साथ जोड़ा जाता है।
- Testing: इसमें यूनिट टेस्टिंग आसान होती है क्योंकि हर छोटे भाग की जांच अलग-अलग की जा सकती है।
- Advantages: इसमें कोड का पुन: उपयोग (code reusability) संभव होता है और मॉड्यूल्स एक-दूसरे पर ज्यादा निर्भर नहीं होते।
- Disadvantages: क्योंकि पूरे सिस्टम का डिज़ाइन बाद में बनता है, इसलिए इंटीग्रेशन में थोड़ा समय लग सकता है।
- Eaxmple: जैसे पहले छोटे-छोटे फ़ंक्शन (
add(),subtract()) बनाएँ, फिर उन्हें जोड़कर कैलकुलेटर प्रोग्राम तैयार करें।